您现在的位置是:主页 > news > 长沙做网站a微联讯点很好/室内设计培训班学费一般多少
长沙做网站a微联讯点很好/室内设计培训班学费一般多少
![]() admin2025/5/2 5:42:35【news】
admin2025/5/2 5:42:35【news】
简介长沙做网站a微联讯点很好,室内设计培训班学费一般多少,天元建设集团有限公司财报,网站建设推广重要性Factorization Machine是对Logistic Regression算法的扩展,是一种基于矩阵分解的机器学习算法。由于逻辑回归只能处理线性可分的二分类算法,对于非线性可分的二分类问题,基本的逻辑回归算法不能很好的进行分类。 目前,被广泛的应…
Factorization Machine是对Logistic Regression算法的扩展,是一种基于矩阵分解的机器学习算法。由于逻辑回归只能处理线性可分的二分类算法,对于非线性可分的二分类问题,基本的逻辑回归算法不能很好的进行分类。
目前,被广泛的应用于广告预估模型中,是一种不错的CTR预估模型,与Logistic Regression相比, FM能够把握一些组合的高阶特征,因此拥有更强的表现力。
目录
1. 因子分解机FM模型
1.1模型的基本形式
1.2 交叉项系数
1.3 二分类因子分解机的损失函数:
1.4 模型的求解:
2. FM算法流程:
3. python实现FM
1. 因子分解机FM模型
1.1模型的基本形式
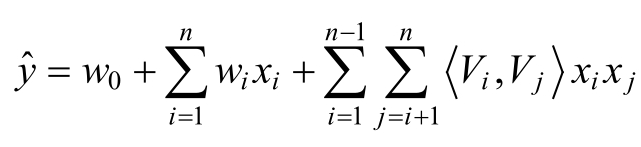
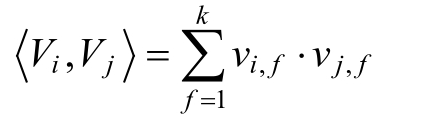
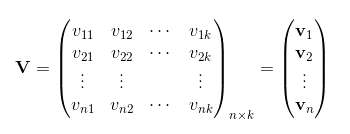
其中,参数表示的是两个大小为k的向量Vi和Vj的点积, k为因子分解机的度。在因子分解机机FM模型中,前面两部分是传统的线性模型,最后一部分将两个互异特征分量之间的相互关系考虑进来。
1.2 交叉项系数
在基本线性回归模型的基础上引入交叉项,如下:
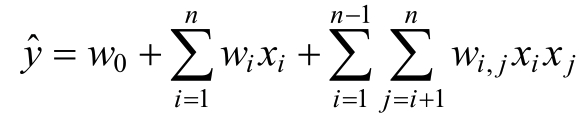
其中:
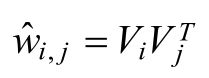
为了求解组合参数, 对每个特征分量
引入k维(k远小于n) 的辅助向量
, 然后利用向量内积的结果
来表示原来的组合参数
FM为每个特征学习了一个隐权重向量(latent vector)。在特征交叉时,使用两个特征隐向量的内积作为交叉特征的权重。
将组合参数进行分解的好处:
- 从原来要求n(n-1)/2个组合参数变成了求矩阵V,参数数量变为n*k.
- 削弱了高阶参数间的独立性:k越大(即对特征分量的表征能力越强),高阶参数间独立性越强,模型越精细;k越小,泛化能力越强,
使用辅助向量乘积表示组合参数的原理:
通常,由于数据稀疏,本来组合参数是学习不到的,但是我们可以通过特征i与其他特征的数据的关系,特征j和其他特征的关系,分别学习到特征i和特征j的对应的辅助向量和
,这样利用
来表示
,便可以解决数据稀疏带来的问题。
1.3 二分类因子分解机的损失函数:
1.4 模型的求解:
对于交叉项 的求解,可以采用公式:
具体过程如下:
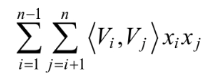

基于随机梯度下降的方式对损失函数求导:
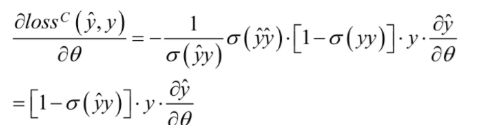
其中:
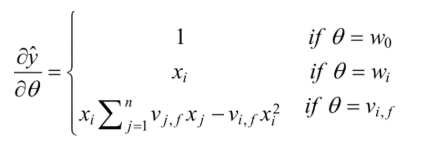
2. FM算法流程:
1.初始化权重w0,w1,....wn和V
2.对每一个样本:
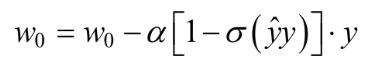
对特征i∈{1,.....n}:
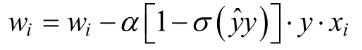
3.重复步骤2,直到满足终止条件
3. python实现FM
import numpy as np
from random import normalvariatedef loadDataSet(data):'''导入训练数据input: data(string)训练数据output: dataMat(list)特征labelMat(list)标签'''dataMat = []labelMat = []with open(data) as fr:for line in fr.readlines():lines = line.strip().split("\t")lineArr = []for i in range(len(lines) - 1):lineArr.append(float(lines[i]))dataMat.append(lineArr)labelMat.append(float(lines[-1]) * 2 - 1) # 转换成{-1,1}return dataMat, labelMatdef sigmoid(inx):return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inx))def initialize_v(n, k):'''初始化交叉项input: n(int)特征的个数k(int)FM模型的超参数output: v(array):交叉项的系数权重'''v = np.zeros((n, k))for i in range(n):for j in range(k):# 利用正态分布生成每一个权重v[i, j] = normalvariate(0, 0.2)return vdef stocGradAscent(dataMatrix, classLabels, k, max_iter, alpha):'''利用随机梯度下降法训练FM模型input: dataMatrix(array)特征classLabels(array)标签k(int)v的维数max_iter(int)最大迭代次数alpha(float)学习率output: w0(float),w(array),v(array):权重'''m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix)# 1、初始化参数w = np.zeros((n, 1)) # 其中n是特征的个数w0 = 0 # 偏置项v = initialize_v(n, k) # 初始化V# 2、训练for it in range(max_iter):for x in range(m): # 随机优化,对每一个样本而言的inter_1 = np.matmul(dataMatrix[x], v)inter_2 = np.matmul(dataMatrix[x] * dataMatrix[x], v * v) # multiply对应元素相乘# 完成交叉项interaction = np.sum(inter_1 * inter_1 - inter_2) / 2.p = w0 + np.matmul(dataMatrix[x] , w) + interaction # 计算预测的输出loss = sigmoid(classLabels[x] * p[0]) - 1w0 = w0 - alpha * loss * classLabels[x]for i in range(n):if dataMatrix[x, i] != 0:w[i, 0] = w[i, 0] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * dataMatrix[x, i]for j in range(k):v[i, j] = v[i, j] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * \(dataMatrix[x, i] * inter_1[j] - \v[i, j] * dataMatrix[x, i] * dataMatrix[x, i])# 计算损失函数的值if it % 1000 == 0:print("\t------ iter: ", it, " , cost: ", \getCost(getPrediction(np.mat(dataMatrix), w0, w, v), classLabels))# 3、返回最终的FM模型的参数return w0, w, vdef getCost(predict, classLabels):'''计算预测准确性input: predict(list)预测值classLabels(list)标签output: error(float)计算损失函数的值'''m = len(predict)error = 0.0for i in range(m):error -= np.log(sigmoid(predict[i] * classLabels[i]))return errordef getPrediction(dataMatrix, w0, w, v):'''得到预测值input: dataMatrix(array)特征w(int)常数项权重w0(int)一次项权重v(float)交叉项权重output: result(list)预测的结果'''m = np.shape(dataMatrix)[0]result = []for x in range(m):inter_1 = dataMatrix[x] * vinter_2 = np.multiply(dataMatrix[x], dataMatrix[x]) * \np.multiply(v, v) # multiply对应元素相乘# 完成交叉项interaction = np.sum(np.multiply(inter_1, inter_1) - inter_2) / 2.p = w0 + dataMatrix[x] * w + interaction # 计算预测的输出pre = sigmoid(p[0, 0])result.append(pre)return resultdef getAccuracy(predict, classLabels):'''计算预测准确性input: predict(list)预测值classLabels(list)标签output: float(error) / allItem(float)错误率'''m = len(predict)allItem = 0error = 0for i in range(m):allItem += 1if float(predict[i]) < 0.5 and classLabels[i] == 1.0:error += 1elif float(predict[i]) >= 0.5 and classLabels[i] == -1.0:error += 1else:continuereturn float(error) / allItemdef save_model(file_name, w0, w, v):'''保存训练好的FM模型input: file_name(string):保存的文件名w0(float):偏置项w(array):一次项的权重v(array):交叉项的权重'''f = open(file_name, "w")# 1、保存w0f.write(str(w0) + "\n")# 2、保存一次项的权重w_array = []m = np.shape(w)[0]for i in range(m):w_array.append(str(w[i, 0]))f.write("\t".join(w_array) + "\n")# 3、保存交叉项的权重m1, n1 = np.shape(v)for i in range(m1):v_tmp = []for j in range(n1):v_tmp.append(str(v[i, j]))f.write("\t".join(v_tmp) + "\n")f.close()if __name__ == "__main__":# 1、导入训练数据print("---------- 1.load data ---------")dataTrain, labelTrain = loadDataSet("data.txt")print("---------- 2.learning ---------")# 2、利用随机梯度训练FM模型w0, w, v = stocGradAscent(np.array(dataTrain), labelTrain, 3, 10000, 0.01)predict_result = getPrediction(np.mat(dataTrain), w0, w, v) # 得到训练的准确性print("----------training accuracy: %f" % (1 - getAccuracy(predict_result, labelTrain)))print("---------- 3.save result ---------")# 3、保存训练好的FM模型save_model("weights", w0, w, v)








